Technical Service & Development Manager- PCR INSC
Abstract: Powder coating is an eco-friendly finishing process that offers numerous environmental, economic, and performance benefits. Unlike traditional liquid coatings, powder coatings are solvent-free, emit negligible volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and produce minimal waste. This technology not only enhances the durability and aesthetics of products but also aligns with global sustainability goals by reducing energy consumption and promoting recyclability. This presentation explores the advantages of powder coating, its applications, and its role in fostering a sustainable future.

In recent years, awareness of environmental conservation and pollution prevention has risen steadily. Government regulations and genuine concern for the environment have motivated chemists to modify all types of coatings to reduce environmental impact. The concept of environmental ‘friendliness’ has dramatically changed the way coatings are formulated.
Powder coatings are arguably the most environmentally ‘friendly’ coatings. They do not contain solvents that release hazardous air pollutants (HAPs). During the baking cycle, powder coatings release very low amounts of VOCs. They produce virtually no waste material and contain very few hazardous chemicals. Notably, with recent advancements in technology, the few hazardous chemicals that have found their way into powder coatings are decreasing as they are being replaced with safer materials.
Introduction to Powder Coating:
Powder coating is a finishing technology that can be described as “ground-up dry paint” or “pulverized plastics.” It provides a decorative, aesthetic, and highly protective coating that can be applied to a wide range of products. The polymeric resins used in producing powder coatings are similar to those used in both paints and plastics, comprising a combination of resin, pigment, filler/extender, and various additive materials. Powder coatings can be either thermoplastic or thermosetting.
The primary difference between these three types lies in the molecular weight range of the polymers used as binders. Plastics use the highest molecular weight resins, paints use the next highest, and powder coatings use the lowest.
The powder coating process involves spraying finely ground, electrostatically or friction-statically charged particles of pigments and resin onto a surface to be coated. The charged powder adheres to the electrically grounded surfaces and is then heated and fused into a smooth coating in a curing oven.
Comparison with traditional Liquid Coatings:
Powder coatings offer several advantages over traditional liquid coatings, particularly in terms of environmental, economic, and performance benefits. Environmentally, powder coatings emit low to zero volatile organic compounds (VOCs) since they do not contain solvents, thereby reducing air pollution and health risks.  They also generate minimal waste due to high transfer efficiency and the ability to recycle unused powder. Additionally, powder coatings are energy-efficient, requiring faster curing times and lower temperatures, and they do not need water for application or cleanup, further reducing environmental impact.
They also generate minimal waste due to high transfer efficiency and the ability to recycle unused powder. Additionally, powder coatings are energy-efficient, requiring faster curing times and lower temperatures, and they do not need water for application or cleanup, further reducing environmental impact.
Economically, powder coatings lead to cost savings through reduced material waste, lower energy costs, and decreased labor expenses. They also provide superior durability and longevity, offering enhanced resistance to chipping, scratching, and corrosion, which extends the lifespan of coated products. Moreover, powder coatings comply with environmental regulations without necessitating costly adjustments. Performance-wise, powder coatings deliver a durable finish that resists physical damage and environmental factors, while also providing a smooth, uniform aesthetic with a wide range of color options. Their versatility makes them suitable for various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.
resistance to chipping, scratching, and corrosion, which extends the lifespan of coated products. Moreover, powder coatings comply with environmental regulations without necessitating costly adjustments. Performance-wise, powder coatings deliver a durable finish that resists physical damage and environmental factors, while also providing a smooth, uniform aesthetic with a wide range of color options. Their versatility makes them suitable for various materials, including metals, plastics, and composites.

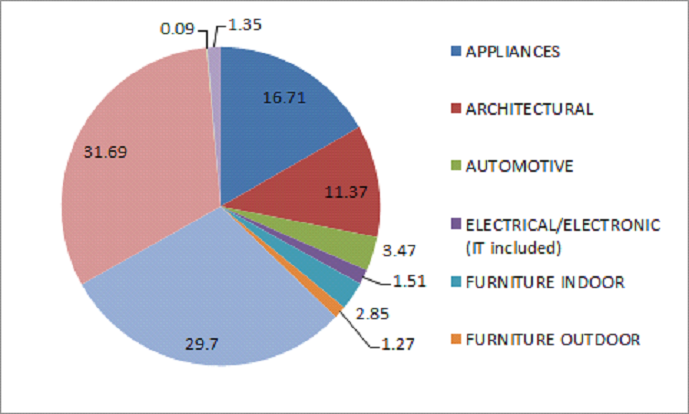
Applications of Powder Coating and market size:X
Powder coating is a versatile finishing technology widely used across various industries due to its durability, aesthetic appeal, and environmental benefits. In the automotive industry, powder coating is applied to wheels, engine parts, and body panels to enhance corrosion resistance and provide a high-quality finish. The consumer goods sector utilizes powder coating for appliances, furniture, and fitness equipment, ensuring long-lasting and visually appealing products. In architecture and construction, powder coating is used on aluminum extrusions, fencing, and metal frameworks to protect against weathering and wear. The electronics industry benefits from powder coating for enclosures and components, offering insulation and protection from environmental factors. Additionally, industrial machinery and equipment often feature powder-coated parts to withstand harsh operating conditions and extend their service life. This technology’s adaptability to different materials and its eco-friendly nature make it a preferred choice for many applications.
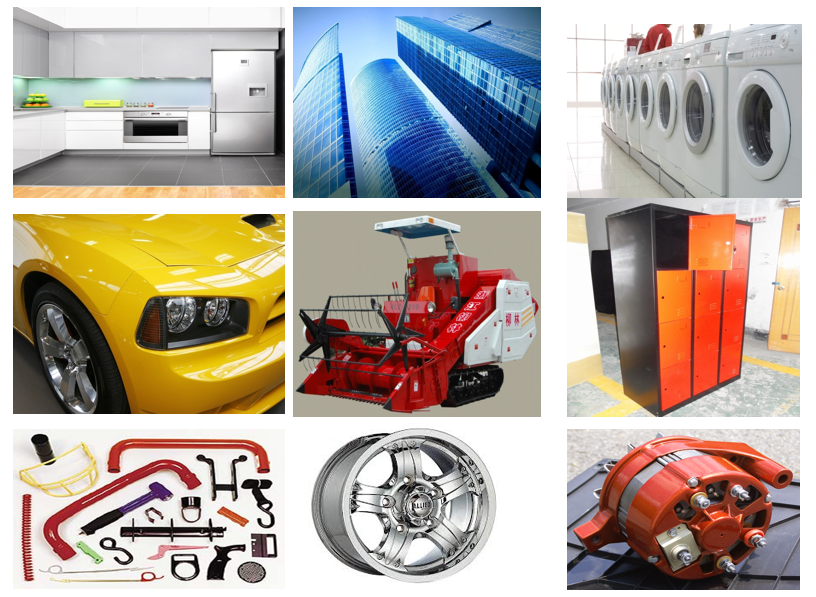

- Automotive industry
- Consumer goods (e.g., appliances, furniture)
- Architectural and construction materials
- Electronics and electrical components
Future Trends, Innovations and Challenges:
The future of powder coating technology is poised for significant advancements driven by sustainability, innovation, and evolving market demands. Key trends include the development of eco-friendly and low-VOC formulations, which align with global environmental regulations and reduce the carbon footprint. few innovations in technologies are:
- UV Curable Powders
- LTC Powder Coatings
- ULB-ACURE Powder Coatings
Innovations in materials science are leading to the creation of high-performance coatings that offer enhanced durability, flexibility, and resistance to extreme conditions. Automation and digitalization are transforming application processes, with smart systems improving efficiency, reducing waste, and ensuring consistent quality. However, challenges remain, such as addressing the limitations of powder coatings on heat-sensitive substrates and improving the recyclability of powder materials. Additionally, the industry must overcome technical hurdles related to achieving uniform coatings on complex geometries and further reducing energy consumption during curing processes. As these innovations continue to evolve, the powder coating industry is set to play a crucial role in sustainable manufacturing and high-performance applications.
Conclusion:
While other eco-friendly technologies like water-based coatings, high-solid coatings, UV-curable coatings, and electrocoating offer significant environmental benefits, powder coating stands out for its combination of low environmental impact, high performance, and versatility.
Each technology has its own strengths and is suitable for different applications, but powder coating’s unique advantages make it a compelling choice for sustainable manufacturing.
Author Introduction:
Dr. Gaurav Chandra Srivastav, was awarded Ph.D. in Chemical Synthesis by Indian Institute of Technology working on “Controlled Radical Polymerization”.
With over 19 years of experience in the Paints-Coatings and Ink Industry, brings expertise in Physical Chemistry, Surface Chemistry, Chemical Reactions and Mechanism with his role as development of new formulations, study on new raw materials and synthesis. Dr. Gaurav owns numerous patents, research papers and authors in-depth technical articles for knowledge enhancement and awareness.

Dr. Gaurav worked with many prominent companies in past and now working as Technical Service & Development Manager- India Subcontinent (Powder Coating Resins) in Allnex Resins for development of technology, technical services and business development.

 Dr. Gaurav Chandra Srivastav
Dr. Gaurav Chandra Srivastav