India, which is expected to reach USD 16.37 billion by 2030 at a CAGR of 9.38%, paints and coatings market, is seeing a boost in smart coatings—technologically advanced materials that respond to environmental changes such as temperature, light, or corrosion.
With construction and automotive segments leading economic growth, the coatings, with self-healing, anti-corrosion, and energy-efficient properties, are set to revolutionize industrial uses.
Though India’s market is prepared through demand and innovation, skills shortages and costs are hurdles to mass adoption.
India’s construction sector, which is projected to reach USD 1.4 trillion by 2025, is driven by urbanization and projects such as the Smart Cities Mission and Gujarat’s Gift City, supported by USD 9.81 billion.
Intelligent coatings improve building longevity and performance, with self-cleaning coatings lowering upkeep expenses on skyscraper glass facades. Thermal-regulating coatings, employing glass microspheres and titanium dioxide nanoparticles, reduce heat intake by as much as 20%, according to a 2024 Hong Kong Polytechnic University report.
Corrosion-resistant coatings shield infrastructure such as bridges, crucial as highway building hit 36.4 km a day in 2021.
The automotive industry, manufacturing 22.93 million vehicles in FY 2021-22, is another primary adopter. Self-healing and anti-corrosion coatings increase vehicle lifespan and lower maintenance expenditures.
Polyurethane-based e-coatings, which account for 92% of auto primers, ensure high gloss and scratch resilience, as observed in the application of Kansai Nerolac to Guangzhou Automobile Group. As electric vehicle (EV) manufacturing is expected to reach 17 million units per year by 2030, plastic substrates’ lightweight smart coatings are demanded, driving market growth.
Indian paint majors are driving innovation. Asian Paints, commanding 75% of the decorative paints market, has self-cleaning, low-VOC coatings that keep in step with sustainable trends. Kansai Nerolac’s waterborne e-coatings minimize environmental footprint, while Nippon Paint’s Smart Road Marking Paint, which was featured at CIIE 2024, improves visibility for intelligent transportation.
AkzoNobel’s partnership with Qlayers ensures automated coating application for uniformity. Nanova Care Coat and Nasiol India, among the startups, are creating nanotechnology-based coatings that possess superhydrophobic as well as antimicrobial functionalities, serving the both industries.
Government initiatives provide strength to preparedness. The Production-Linked Incentive (PLI) scheme promotes R&D of advanced materials, and the National Research Foundation (NRF) spends Rs. 50,000 crore on industry-academia collaboration.
The Raising and Accelerating MSME Performance (RAMP) program helps smaller enterprises, with a 23% market share, implement smart coatings. The National Green Mission encourages low-VOC compositions, based on worldwide ESG norms.
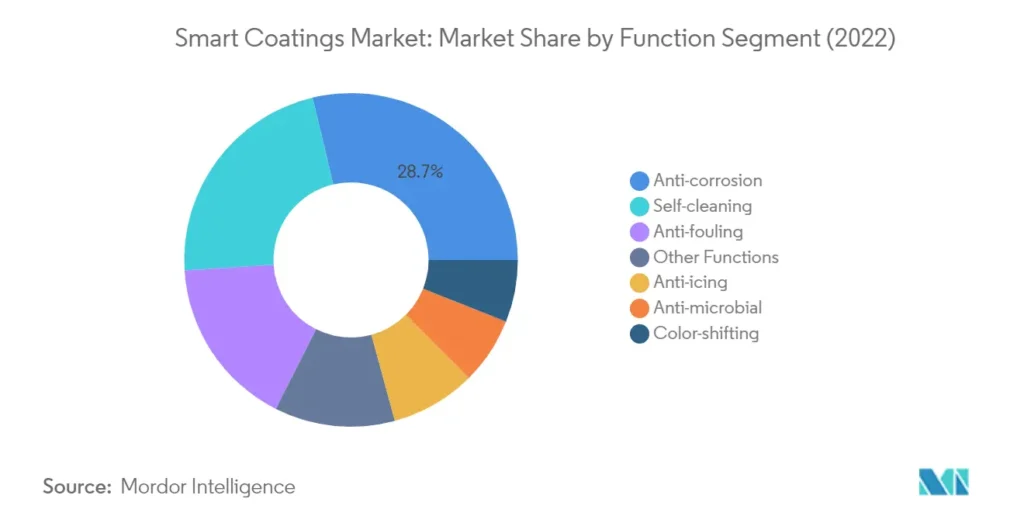
Construction, with a 25.6% market share in smart coatings in 2024, and automotive industries gain immensely from such programs.
Exorbitant prices, though, are a deterrent. Intelligent coatings, 20-30% more expensive than traditional ones, put MSME budgets under pressure, with merely 10% embracing such technologies, according to a 2024 SIDBI report. Skilling gaps are severe—only 5% of the labor force is skilled in applications of nanotechnology, according to Nasscom. Infrastructure issues, such as uneven power supply in Tier 2 towns, interrupt manufacturing.
Regulatory lag, with patent grants within 4-6 years compared with China’s 2 years, slows down innovation. Rural market low awareness further slows down adoption.
Experts propound targeted interventions to boost preparedness. Subsidies from the Technology Upgradation Scheme can reduce the costs for MSMEs.
Scaling up Skill India’s vocational training in nanotechnology can close the skill gap.
Streamlining patent processes and improving rural 5G connectivity will support production and awareness. Public-private partnerships, like BASF’s Mangalore Coatings Technology Center, can scale R&D.
Awareness campaigns by CII can drive demand in smaller cities, while meeting global sustainability standards will boost exports.
With the market for smart coatings expected to increase from USD 9.17 billion in 2024 to USD 57.58 billion by 2033 at a 22.64% CAGR, India’s construction and automobile industries are poised to benefit from these technologies.
By overcoming barriers in cost, skills, and infrastructure, India can facilitate inclusive adoption, especially for MSMEs.
As India aims for a USD 1.4 trillion construction industry and 17 million EV sales in 2030, smart coatings are a way to sustainability and resilience—if India can bring its ecosystem into sync with this transformational potential.
