The Indian subcontinent is known for its heavy reliance on the annual monsoon rains, which play a crucial role in sustaining agriculture and ensuring water availability for millions of people. However, the latest weather reports are causing concerns as meteorologists predict a stronger El Niño event, which could potentially dampen the monsoon prospects for the upcoming season. The impact of El Niño on the Indian monsoon has been well-documented in the past, and its intensification raises fears of drought-like conditions and adverse effects on the economy. In this article, we delve into the implications of a stronger El Niño on the monsoon, agricultural sector, and overall socio-economic landscape of India.
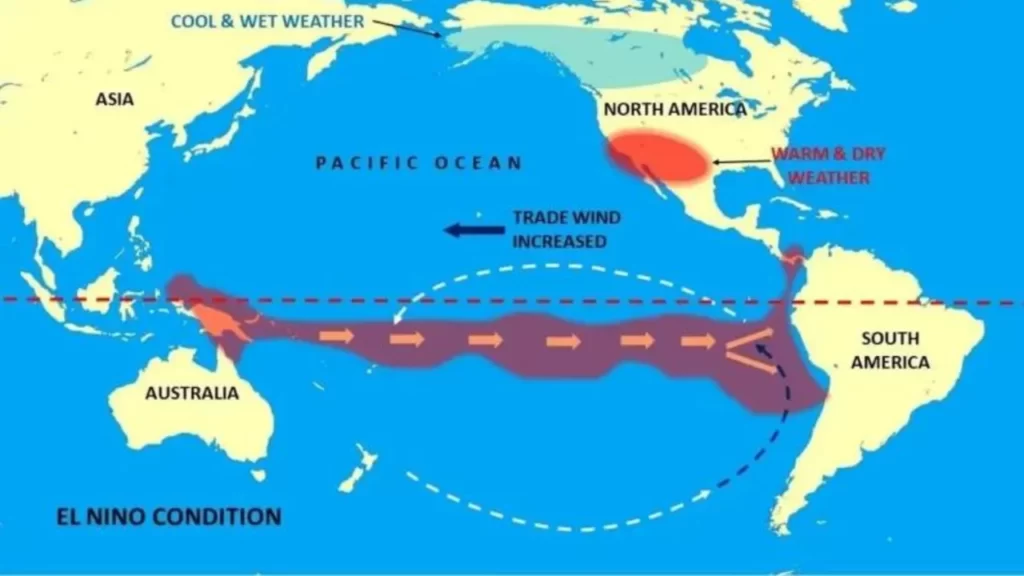
El Niño and Its Influence on the Indian Monsoon
El Niño refers to a climate pattern characterized by the warming of the central and eastern tropical Pacific Ocean, leading to significant atmospheric changes worldwide. This phenomenon has far-reaching effects on weather patterns, including the Indian monsoon. Typically, El Niño events result in below-average rainfall in India, while the opposite phenomenon, La Niña, tends to enhance the monsoon.
Experts have warned that the intensity of the upcoming El Niño is expected to be stronger than usual, potentially disrupting the normal monsoon cycle. The weakening of the monsoon can have severe consequences for Indian agriculture, as a significant portion of the country’s farmland is rain-fed. Insufficient rainfall could lead to water scarcity, reduced crop yields, and increased vulnerability for farmers.
Impact on Agriculture and Food Security
India’s agricultural sector heavily depends on the monsoon for irrigation and crop cultivation. A weak monsoon due to El Niño can hamper agricultural productivity and pose challenges to food security. Crops like rice, sugarcane, and oilseeds, which require ample water, are particularly susceptible to drought-like conditions. Reduced yields can lead to higher food prices, affecting both rural and urban populations.
Moreover, the agricultural sector contributes significantly to India’s economy, with millions of livelihoods dependent on farming. A dip in agricultural output could lead to economic distress, rural unemployment, and migration to already overcrowded urban areas. The repercussions would not be limited to the farming community alone but would reverberate throughout the economy.
Mitigation Measures and Adaptation Strategies
Recognizing the potential risks associated with a stronger El Niño, the Indian government and various stakeholders need to proactively implement measures to mitigate its impact. Some of the steps that can be taken include:
- Improving irrigation infrastructure: Enhancing irrigation facilities, promoting efficient water management, and investing in modern irrigation techniques can help reduce dependence on monsoon rains and ensure a more stable water supply for crops.
- Crop diversification and climate-resilient practices: Encouraging farmers to diversify crops and adopt climate-resilient practices, such as rainwater harvesting, mulching, and crop rotation, can help mitigate the risks associated with weak monsoons.
- Promoting agricultural insurance: Expanding the reach of crop insurance schemes and ensuring timely compensation for crop losses can provide a safety net for farmers during periods of drought and encourage them to adopt risk-reducing measures.
- Enhancing weather forecasting capabilities: Strengthening meteorological infrastructure, improving weather forecasting models, and disseminating accurate and timely information to farmers can help them make informed decisions regarding planting schedules and resource allocation.
